| 金融风控、公安刑侦、社会关系、人脉分析等需求分析与数据库实现 原作者:digoal/德哥 创作时间:2016-12-13 23:20:17+08 |
doudou586 发布于2016-12-17 23:20:17
 评论: 4 评论: 4
 浏览: 45942 浏览: 45942
|
金融风控、公安刑侦、社会关系、人脉分析等需求分析与数据库实现 - PostgreSQL图数据库场景应用
作者: digoal
日期: 2016-12-13
标签: PostgreSQL, pgrouting, neo4j, graph database, 图数据库, 金融风险控制, 风控, 刑侦, 社会关系, 近亲, linkedin, 人脉
背景
人类是群居动物,随着人口的增长,联络方式越来越无界化,人与人,人与事件,人与时间之间形成了一张巨大的关系网络。
有许多场景就是基于这张巨大的关系网络的,比如。
1. 猎头挖人
作为IT人士或者猎头、HR,对Linkedin一定不陌生,领英网实际上就是一个维护人际关系的网站。
通过搜索你的一度人脉,可以找到与你直接相关的人,搜索2度人脉,可以搜索到与你间接相关的人。
当然你还可以继续搜索N度人脉,不过那些和你可能就不那么相关了。
如果你知道和美女范冰冰隔了几度人脉,是不是有点心动了呢?
其实在古代,就有这种社会关系学,还有这种专门的职业,买官卖官什么的,其实都是人脉关系网。看过红楼梦的话,你会发现那家子人怎么那么多亲戚呢?
2. 公安破案
公安刑侦学也是一类人脉相关的应用,只是现在的关系和行为越来越复杂,这种关系也越来越复杂,原来的人能接触的范围基本上就靠2条腿,顶多加匹马。
现在,手机,电脑,ATM机,超时,摄像头,汽车等等,都通过公路网、互联网连接在一起。
一个人的行为,产生的关系会更加的复杂,单靠人肉的关系分析,刑侦难度变得越来越复杂。
3. 金融风控
比如银行在审核贷款资格时,通常需要审核申请人是否有偿还能力,是否有虚假消息,行为习惯,资产,朋友圈等等。 同样涉及到复杂的人物关系,人的行为关系分析等等。
图片来自互联网

此类围绕人为中心,事件为关系牵连的业务催生了图数据库的诞生。
目前比较流行的图数据库比如neo4j,等。
详见: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graph_database
PostgreSQL是一个功能全面的数据库,其中就有一些图数据库产品的后台是使用PostgreSQL的,例如OpenCog, Cayley等。
除了这些图数据库产品,PostgreSQL本身在关系查询,关系管理方面也非常的成熟。
本文将给大家揭示PostgreSQL是如何玩转金融风控,刑侦,社会关系,人脉关系需求的。
图数据模型
在许多图数据库的设计中会将事件或人物作为NODE,事件或人物之间如果有关系,则建立关系。
在PostgreSQL中,我们可以使用2列来表示这种关系,每列代表一个事件或人物,如果两者有关系,就创建一条记录。
这样表示,和图数据保持一致。
当然后面还有优化的手段,比如数组,PostgreSQL中,将与一个事件关联的其他事件或人物作为数组来存储,可以提高检索的效率。
PostgreSQL 递归查询能满足关系推导的需求吗
PostgreSQL 递归查询是很出彩的功能,还记不记得我写的, 《distinct xx和count(distinct xx)的变态递归优化方法 - 索引收敛(skip scan)扫描》 ,《用PostgreSQL找回618秒逝去的青春 - 递归收敛优化》
但是,请记住,关系是可能打环的,由于有LOOP的问题,所以在推导时每次要排除之前已找到的所有关系,这一点目前的PostgreSQL递归还没有办法做到。
例如,我需要这样的语法来支持排除打环
postgres=# with recursive s as (
select c1,c2 from a where c1=1
union all
select a.c1,a.c2 from a join s on (a.c1=s.c2) where a.c1 not in (
with t as (insert into tmp select * from s)
select c2 from tmp ) and s.* is not null
)
select * from s;
ERROR: 42P19: recursive reference to query "s" must not appear within a subquery
LINE 4: ... not in (with t as (insert into tmp select * from s) select ...
^
LOCATION: checkWellFormedRecursionWalker, parse_cte.c:773
而目前是不支持的.
递归只能排除work table的集合,不能排除整个递归过程的集合,如果关系中存在LOOP则会导致无限LOOP。
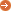
图例 :
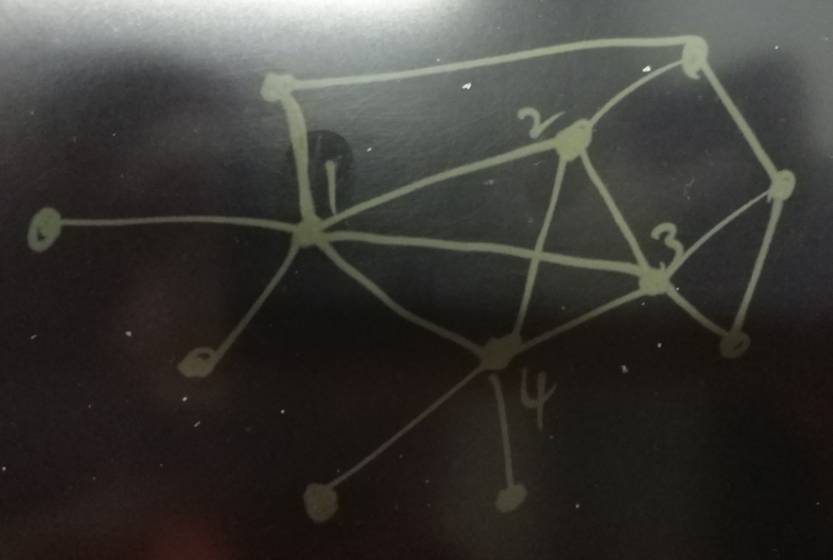

这里的很多点合在一起就形成环状了,例如我和A是好朋友,和B也是好朋友,A和B也是好朋友,这样的关系。
在推导时,从我开始推导出A,B,然后A又推导出B,B又推导出A,。。。。无限循环。
PostgreSQL UDF解决关系环的问题
使用UDF可以很好的解决数据打环导致递归无限循环的这个问题
建模
构建1亿条关系数据,假设人物一共1000万个。此处为了测试方便,在表中省略人物或事件的其他属性(如时间,地点,亲密度等)
postgres=# create table a(c1 int, c2 int, primary key(c1,c2)); CREATE TABLE postgres=# create index idx_a_1 on a(c1); CREATE INDEX postgres=# create index idx_a_2 on a(c2); CREATE INDEX postgres=# insert into a select random()*10000000, random()*10000000 from generate_series(1,100000000) ;
函数用到的几个临时表
create temp table if not exists tmp1(level int, c1 int, c2 int) ON COMMIT delete rows; create index if not exists idx_tmp1_1 on tmp1(level); create index if not exists idx_tmp1_2 on tmp1(c1); create index if not exists idx_tmp1_3 on tmp1(c2); create unlogged table u1 (like tmp1); create temp table if not exists tmp2(level int, path int[], c1 int, c2 int) ON COMMIT delete rows; create index if not exists idx_tmp2_1 on tmp2(level); create index if not exists idx_tmp2_2 on tmp2(c1); create index if not exists idx_tmp2_3 on tmp2(c2); create unlogged table u2 (like tmp2);
函数1, 输出以A为中心的,N级关系数据。
create or replace function find_rel(v_c1 int, v_level int) returns setof u1 as $$
declare
i int := 1;
begin
if v_level <=0 then
raise notice 'level must >=1';
return;
end if;
-- 9.6还是inner temp table,频繁创建和删除,可能导致catalog产生垃圾,需要注意一下。
-- 用来临时存储从起点开始, 牵扯出来的每一层级的关系
create temp table if not exists tmp1(level int, c1 int, c2 int) ON COMMIT delete rows;
create index if not exists idx_tmp1_1 on tmp1(level);
create index if not exists idx_tmp1_2 on tmp1(c1);
create index if not exists idx_tmp1_3 on tmp1(c2);
-- 存储初始层级, 即起点的数据
return query insert into tmp1 select i, * from a where c1=v_c1 returning *;
loop
i := i+1;
-- 已找到所有层级的数据
if i > v_level then
return;
end if;
-- 通过与level=i-1的JOIN推导下一级关系(group by排除重复node(比如1-2-3-4, 1-5-3-4,这里的3会被排除掉)),
-- 通过not exists排除打环的点
return query insert into tmp1 select i, a.c1, a.c2 from a join
(select c2 from tmp1 where level=i-1 group by c2) tmp on (a.c1=tmp.c2)
where not exists (select 1 from tmp1 where a.c1 = tmp1.c1) returning *;
end loop;
end;
$$ language plpgsql strict;
函数2, 输出以A为中心的,N级关系数据。
同时产生路径,注意这个路径是完备路径,一个NODE可能有多条线路经过。
create or replace function find_rel_withpath(v_c1 int, v_level int) returns setof u2 as $$
declare
i int := 1;
begin
if v_level <=0 then
raise notice 'level must >=1';
return;
end if;
-- 9.6还是inner temp table,频繁创建和删除,可能导致catalog产生垃圾,需要注意一下。
-- 用来临时存储从起点开始, 牵扯出来的每一层级的关系
create temp table if not exists tmp2(level int, path int[], c1 int, c2 int) ON COMMIT delete rows;
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_1 on tmp2(level);
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_2 on tmp2(c1);
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_3 on tmp2(c2);
-- 存储初始层级, 即起点的数据
return query insert into tmp2 select i, array[]::int[] || c1 || c2 , * from a where c1=v_c1 returning *;
loop
i := i+1;
-- 已找到所有层级的数据
if i > v_level then
return;
end if;
-- 通过与level=i-1的JOIN推导下一级关系(group by排除重复node(比如1-2-3-4, 1-2-3-4,完全重复的路径,排除掉。
-- 实际中加了c1,c2唯一约束后不可能存在)),通过not exists排除打环的点
-- path用来表示当前路径,是不是很爽
-- 如果有c1,c2的PK约束,可以不使用group by,直接与tmp2关联
return query insert into tmp2 select i, tmp.path||a.c2, a.c1, a.c2 from a join
(select c2,path from tmp2 where level=i-1 group by c2,path) tmp on (a.c1=tmp.c2)
where not exists (select 1 from tmp2 where a.c1 = tmp2.c1) returning *;
end loop;
end;
$$ language plpgsql strict;
函数3,找两个人物、事件的最短关系路径
这里就考验优化算法了,涉及从哪个点开始搜索,或者两边同时进行辐射式搜索等。
create or replace function find_rel_path(v_c1 int, v_c2 int) returns setof int[] as $$
declare
i int := 1;
begin
-- 9.6还是inner temp table,频繁创建和删除,可能导致catalog产生垃圾,需要注意一下。
-- 用来临时存储从起点开始, 牵扯出来的每一层级的关系
create temp table if not exists tmp2(level int, path int[], c1 int, c2 int) ON COMMIT delete rows;
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_1 on tmp2(level);
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_2 on tmp2(c1);
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_3 on tmp2(c2);
-- 存储初始层级, 即起点的数据
insert into tmp2 select i, array[]::int[] || c1 || c2 , * from a where c1=v_c1;
loop
i := i+1;
perform 1 from tmp2 where c2=v_c2 limit 1;
if found then
return query select path from tmp2 where c2=v_c2 and level=i-1;
return;
end if;
insert into tmp2 select i, tmp.path||a.c2, a.c1, a.c2 from a join
(select c2,path from tmp2 where level=i-1 group by c2,path) tmp on (a.c1=tmp.c2)
where not exists (select 1 from tmp2 where a.c1 = tmp2.c1);
end loop;
end;
$$ language plpgsql strict;
测试
1. 找出ID=1这个用户的3级关系网
select * from find_rel(1,3); select * from find_rel_withpath(1,3);
结果
postgres=# select * from find_rel(1,3);
NOTICE: relation "tmp1" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp1_1" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp1_2" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp1_3" already exists, skipping
level | c1 | c2
-------+---------+---------
1 | 1 | 5157873
1 | 1 | 3102468
1 | 1 | 8399312
1 | 1 | 1442141
1 | 1 | 5094441
1 | 1 | 1521897
1 | 1 | 401079
2 | 401079 | 1147078
2 | 401079 | 9740100
......
3 | 1731998 | 6503196
3 | 1731998 | 5112396
3 | 6525458 | 937613
3 | 6525458 | 8459123
3 | 6525458 | 8419231
3 | 6525458 | 4021987
(828 rows)
Time: 15.000 ms
postgres=# select * from find_rel_withpath(1,3);
NOTICE: relation "tmp2" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_1" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_2" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_3" already exists, skipping
level | path | c1 | c2
-------+-----------------------------+---------+---------
1 | {1,5157873} | 1 | 5157873
1 | {1,3102468} | 1 | 3102468
1 | {1,8399312} | 1 | 8399312
1 | {1,1442141} | 1 | 1442141
1 | {1,5094441} | 1 | 5094441
1 | {1,1521897} | 1 | 1521897
1 | {1,401079} | 1 | 401079
2 | {1,401079,1147078} | 401079 | 1147078
2 | {1,401079,9740100} | 401079 | 9740100
......
3 | {1,1442141,9719411,7811631} | 9719411 | 7811631
3 | {1,401079,9740100,5119416} | 9740100 | 5119416
3 | {1,401079,9740100,350046} | 9740100 | 350046
3 | {1,401079,9740100,8223067} | 9740100 | 8223067
3 | {1,401079,9740100,5608312} | 9740100 | 5608312
3 | {1,401079,9740100,7920319} | 9740100 | 7920319
3 | {1,401079,9740100,6416565} | 9740100 | 6416565
(828 rows)
Time: 19.524 ms
postgres=# select * from find_rel_withpath(1,5) order by level desc limit 10;
NOTICE: relation "tmp2" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_1" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_2" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_3" already exists, skipping
level | path | c1 | c2
-------+----------------------------------------+-----+---------
5 | {1,401079,3806993,3879310,165,8074824} | 165 | 8074824
5 | {1,401079,3806993,3879310,165,5983603} | 165 | 5983603
5 | {1,401079,3806993,3879310,165,9804825} | 165 | 9804825
5 | {1,401079,3806993,3879310,165,3848025} | 165 | 3848025
5 | {1,401079,3806993,3879310,165,2045526} | 165 | 2045526
5 | {1,401079,3806993,3879310,165,9783524} | 165 | 9783524
5 | {1,401079,3806993,3879310,165,386886} | 165 | 386886
5 | {1,401079,3806993,3879310,165,6318408} | 165 | 6318408
5 | {1,401079,3806993,3879310,165,1150578} | 165 | 1150578
5 | {1,401079,3806993,3879310,165,6702827} | 165 | 6702827
(10 rows)
Time: 1473.953 ms
2. 找出ID=1和ID=386886的最短关系路径
select * from find_rel_path(1,386886);
结果
postgres=# select * from find_rel_path(1,386886);
NOTICE: relation "tmp2" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_1" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_2" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_3" already exists, skipping
find_rel_path
---------------------------------------
{1,401079,3806993,3879310,165,386886}
(1 row)
Time: 1069.781 ms
postgres=# select * from find_rel_path(1,3879310);
NOTICE: relation "tmp2" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_1" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_2" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_3" already exists, skipping
find_rel_path
----------------------------
{1,401079,3806993,3879310}
(1 row)
Time: 17.290 ms
速度杠杠的。
UDF优化思路1 - 游标,流式接收
我们看到,前面的UDF,都是搜索到所有数据后才开始输出,实际上,可以在找到第一条记录后就开始输出,这样客户端可以不断的接收数据,减少延迟。
使用游标就可以达到这样的目的。
游标用法参考: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.6/static/plpgsql-cursors.html
举例
create or replace function find_rel_withpath_cur(v_c1 int, v_level int) returns setof refcursor as $$
declare
i int := 1;
ref refcursor[];
res refcursor;
begin
if v_level <=0 then
raise notice 'level must >=1';
return;
end if;
for x in 1..v_level loop
ref[x] := 'a'||x;
end loop;
-- 9.6还是inner temp table,频繁创建和删除,可能导致catalog产生垃圾,需要注意一下。
-- 用来临时存储从起点开始, 牵扯出来的每一层级的关系
create temp table if not exists tmp2(level int, path int[], c1 int, c2 int) ON COMMIT delete rows;
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_1 on tmp2(level);
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_2 on tmp2(c1);
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_3 on tmp2(c2);
-- 存储初始层级, 即起点的数据
res := ref[i];
open res for insert into tmp2 select i, array[]::int[] || c1 || c2 , * from a where c1=v_c1 returning *;
return next res;
loop
i := i+1;
-- 已找到所有层级的数据
if i > v_level then
return;
end if;
-- 通过与level=i-1的JOIN推导下一级关系(group by排除重复node(比如1-2-3-4, 1-2-3-4,完全重复的路径,排除掉。
-- 实际中加了c1,c2唯一约束后不可能存在)),通过not exists排除打环的点
-- path用来表示当前路径,是不是很爽
-- 如果有c1,c2的PK约束,可以不使用group by,直接与tmp2关联
res := ref[i];
open res for insert into tmp2 select i, tmp.path||a.c2, a.c1, a.c2 from a join
(select c2,path from tmp2 where level=i-1 group by c2,path) tmp on (a.c1=tmp.c2)
where not exists (select 1 from tmp2 where a.c1 = tmp2.c1) returning *;
return next res;
end loop;
end;
$$ language plpgsql strict;
postgres=# begin;
BEGIN
Time: 0.390 ms
postgres=# select * from find_rel_withpath_cur(1,5);
NOTICE: relation "tmp2" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_1" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_2" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_3" already exists, skipping
find_rel_withpath_cur
-----------------------
a1
a2
a3
a4
a5
(5 rows)
Time: 4.008 ms
返回1级关系
postgres=# fetch all in a1;
level | path | c1 | c2
-------+-------------+----+---------
1 | {1,5157873} | 1 | 5157873
1 | {1,3102468} | 1 | 3102468
1 | {1,8399312} | 1 | 8399312
1 | {1,1442141} | 1 | 1442141
1 | {1,5094441} | 1 | 5094441
1 | {1,1521897} | 1 | 1521897
1 | {1,401079} | 1 | 401079
(7 rows)
Time: 0.958 ms
返回2级关系
postgres=# fetch all in a2;
level | path | c1 | c2
-------+---------------------+---------+---------
2 | {1,401079,1147078} | 401079 | 1147078
2 | {1,401079,9740100} | 401079 | 9740100
2 | {1,401079,8171779} | 401079 | 8171779
2 | {1,401079,3806993} | 401079 | 3806993
2 | {1,401079,2491387} | 401079 | 2491387
......
2 | {1,8399312,5886963} | 8399312 | 5886963
2 | {1,8399312,3652462} | 8399312 | 3652462
2 | {1,8399312,8148713} | 8399312 | 8148713
2 | {1,8399312,8282991} | 8399312 | 8282991
(75 rows)
Time: 3.173 ms
以此类推
postgres=# fetch all in a3;
level | path | c1 | c2
-------+-----------------------------+---------+---------
3 | {1,1521897,47614,2653114} | 47614 | 2653114
3 | {1,1521897,47614,1354306} | 47614 | 1354306
3 | {1,1521897,47614,7452721} | 47614 | 7452721
...
3 | {1,401079,9740100,7920319} | 9740100 | 7920319
3 | {1,401079,9740100,6416565} | 9740100 | 6416565
(746 rows)
Time: 25.455 ms
postgres=# fetch all in a4;
......
4 | {1,401079,8171779,9968575,6388546} | 9968575 | 6388546
4 | {1,401079,8171779,9968575,8281935} | 9968575 | 8281935
4 | {1,401079,8171779,9968575,6076729} | 9968575 | 6076729
4 | {1,401079,8171779,9968575,7087557} | 9968575 | 7087557
(7383 rows)
Time: 14.482 ms
注意
因为这里的游标返回有上下文的关系,所以务必在接收完一个游标后再接收下一个游标的数据,如果一开就就直接接收后面的游标,会没有数据。
postgres=# begin; BEGIN Time: 0.561 ms postgres=# select * from find_rel_withpath_cur(1,5); NOTICE: relation "tmp2" already exists, skipping NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_1" already exists, skipping NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_2" already exists, skipping NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_3" already exists, skipping find_rel_withpath_cur ----------------------- a1 a2 a3 a4 a5 (5 rows) Time: 2.161 ms
如果一开始就跳跃式的接收,那么这个以后的游标都不会再有数据了。
postgres=# fetch all in a4;
level | path | c1 | c2
-------+------+----+----
(0 rows)
Time: 0.738 ms
postgres=# fetch all in a5;
level | path | c1 | c2
-------+------+----+----
(0 rows)
Time: 0.727 ms
postgres=# fetch all in a1;
level | path | c1 | c2
-------+-------------+----+---------
1 | {1,5157873} | 1 | 5157873
1 | {1,3102468} | 1 | 3102468
1 | {1,8399312} | 1 | 8399312
1 | {1,1442141} | 1 | 1442141
1 | {1,5094441} | 1 | 5094441
1 | {1,1521897} | 1 | 1521897
1 | {1,401079} | 1 | 401079
(7 rows)
Time: 0.954 ms
使用游标后,可以按关系层级流式接收了。
c2=数组类型时的游标返回函数
create or replace function find_rel_withpath_cur_array(v_c1 int, v_level int) returns setof refcursor as $$
declare
i int := 1;
ref refcursor[];
res refcursor;
begin
if v_level <=0 then
raise notice 'level must >=1';
return;
end if;
for x in 1..v_level loop
ref[x] := 'a'||x;
end loop;
-- 9.6还是inner temp table,频繁创建和删除,可能导致catalog产生垃圾,需要注意一下。
-- 用来临时存储从起点开始, 牵扯出来的每一层级的关系
create temp table if not exists tmp2(level int, path int[], c1 int, c2 int) ON COMMIT delete rows;
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_1 on tmp2(level);
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_2 on tmp2(c1);
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_3 on tmp2(c2);
-- 存储初始层级, 即起点的数据
res := ref[i];
open res for insert into tmp2 select i as level, array[]::int[] || c1 || c2 as path , c1, c2 from
(select c1,unnest(c2) as c2 from a where c1=v_c1) a returning *;
return next res;
loop
i := i+1;
-- 已找到所有层级的数据
if i > v_level then
return;
end if;
-- 通过与level=i-1的JOIN推导下一级关系(group by排除重复node(比如1-2-3-4, 1-2-3-4,完全重复的路径,排除掉。
-- 实际中加了c1,c2唯一约束后不可能存在)),通过not exists排除打环的点
-- path用来表示当前路径,是不是很爽
-- 如果有c1,c2的PK约束,可以不使用group by,直接与tmp2关联
res := ref[i];
open res for insert into tmp2 select i as level, a.path||a.c2 as path, a.c1, a.c2 from
(select tmp2.path, a.c1, unnest(a.c2) c2 from a join tmp2 on
(a.c1=tmp2.c2 and tmp2.level=i-1 and tmp2.c1<>a.c1)) a returning *;
return next res;
end loop;
end;
$$ language plpgsql strict;
UDF优化思路2,函数流式接收
目前PostgreSQL的insert into ... returning *要等insert结束才能返回第一条记录,所以层级越深,插入时间越长,层级越深的数据接收可能越慢。那么还有更好的优化手段吗。
除了修改内核(这是最好的方法),让其支持insert into ... returning *的游标支持流式返回,还有一种方法,在函数中流式返回。
创建1亿用户,每5万作为一个有牵连的群体,每个用户牵连1000个用户,形成1000亿的超大规模关系网。
postgres=# create table a(c1 int, c2 int[], primary key (c1));
CREATE TABLE
vi test.sql
\set id random(1,100000000)
insert into a select :id, (select array_agg(((width_bucket(:id,1,100000000,2000)-1)*50000 + (random()*50000)::int))
from generate_series(1,1000)) on conflict do nothing;
pgbench -M prepared -n -r -P 5 -f ./test.sql -c 64 -j 64 -T 100000
约520GB
测试场景
根据用户A,推导他的N级关系网。
create or replace function find_rel_withpath_cur(v_c1 int, v_level int) returns setof record as $$
declare
i int := 1;
ref1 cursor(var1 int, var2 int) for select var1 as level, array[]::int[] || c1 || c2 as path , c1, c2 from
(select c1,unnest(c2) as c2 from a where c1=var2) a ;
ref2 cursor(var1 int) for select var1 as level, a.path||a.c2 as path, a.c1, a.c2 from
(select tmp2.path, a.c1, unnest(a.c2) c2 from a join tmp2 on
(a.c1=tmp2.c2 and tmp2.level=i-1 and tmp2.c1<>a.c1)) a;
begin
if v_level <=0 then
raise notice 'level must >=1';
return;
end if;
-- 9.6还是inner temp table,频繁创建和删除,可能导致catalog产生垃圾,需要注意一下。
-- 用来临时存储从起点开始, 牵扯出来的每一层级的关系
-- 目前plpgsql不支持流式返回, 即使使用return next , return query
-- https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.6/static/plpgsql-control-structures.html
create temp table if not exists tmp2(level int, path int[] unique, c1 int, c2 int) ON COMMIT delete rows;
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_1 on tmp2(level, c2);
-- 存储初始层级, 即起点的数据
for rec in ref1(i, v_c1) loop
insert into tmp2 values (rec.level, rec.path, rec.c1, rec.c2) on conflict do nothing;
if found then
return next rec;
end if;
end loop;
loop
i := i+1;
-- 已找到所有层级的数据
if i > v_level then
return;
end if;
-- 通过与level=i-1的JOIN推导下一级关系(group by排除重复node(比如1-2-3-4, 1-2-3-4,完全重复的路径,排除掉。
-- 实际中加了c1,c2唯一约束后不可能存在)),通过not exists排除打环的点
-- path用来表示当前路径,是不是很爽
-- 如果有c1,c2的PK约束,可以不使用group by,直接与tmp2关联
for rec in ref2(i) loop
insert into tmp2 values(rec.level, rec.path, rec.c1, rec.c2) on conflict do nothing;
if found then
return next rec;
end if;
end loop;
end loop;
return;
end;
$$ language plpgsql strict;
目前plpgsql不支持流式返回, 即使使用return next , return query, https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.6/static/plpgsql-control-structures.html
Note: The current implementation of RETURN NEXT and RETURN QUERY stores the entire result set before returning from the function, as discussed above. That means that if a PL/pgSQL function produces a very large result set, performance might be poor: data will be written to disk to avoid memory exhaustion, but the function itself will not return until the entire result set has been generated. A future version of PL/pgSQL might allow users to define set-returning functions that do not have this limitation. Currently, the point at which data begins being written to disk is controlled by the work_mem configuration variable. Administrators who have sufficient memory to store larger result sets in memory should consider increasing this parameter.
目前使用c function实现以上逻辑,可以实现函数的流式接收。
测试场景2
测试从1000亿数据量中,取出某个用户的10级关系
-- 消除重复NODE,例如有N条路径经过同一个NODE,只记录一个NODE。
create or replace function find_rel(v_c1 int, v_level int) returns setof u1 as $$
declare
i int := 1;
begin
if v_level <=0 then
raise notice 'level must >=1';
return;
end if;
-- 9.6还是inner temp table,频繁创建和删除,可能导致catalog产生垃圾,需要注意一下。
-- 用来临时存储从起点开始, 牵扯出来的每一层级的关系
create temp table if not exists tmp1( level int, c1 int primary key) ON COMMIT delete rows;
create index if not exists idx_tmp1_1 on tmp1(level, c1);
-- 存储初始层级, 即起点的数据
return query insert into tmp1 select i, c1 from a where c1=v_c1 union select i, unnest(c2) from a
where c1=v_c1 returning *;
loop
i := i+1;
-- 已找到所有层级的数据
if i > v_level then
return;
end if;
-- 通过与level=i-1的JOIN推导下一级关系(group by排除重复node(比如1-2-3-4, 1-5-3-4,这里的3会被排除掉)),
-- 通过not exists排除打环的点
return query
insert into tmp1
select t.i, t.c2 from
( select i, unnest(c2) c2 from a join tmp1 tmp on ( a.c1=tmp.c1 and tmp.level=i-1 and a.c1<>v_c1 )
) t
left join tmp1 on (t.c2=tmp1.c1)
where tmp1.* is null group by 1,2
on conflict do nothing
returning *;
end loop;
end;
$$ language plpgsql strict;
postgres=# select count(*) from find_rel(5000,10);
NOTICE: relation "tmp1" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp1_1" already exists, skipping
count
-------
50001
(1 row)
由于数据模型的问题,第三级搜索了5000万记录,所以耗费了约15秒,没有打开CPU并行也是耗费时间较长的原因。
据研究,每个人约维护200个左右的亲密关系网正常的业务模型应该是每一级都会加一定的约束进行结果收敛,不会无限扩散。
正常的业务模型,查询时间可以控制在秒级。
Time: 17131.492 ms
create or replace function find_rel_cur(v_c1 int, v_level int) returns setof refcursor as $$
declare
i int := 1;
ref refcursor[];
res refcursor;
begin
if v_level <=0 then
raise notice 'level must >=1';
return;
end if;
for x in 1..v_level loop
ref[x] := 'a'||x;
end loop;
-- 9.6还是inner temp table,频繁创建和删除,可能导致catalog产生垃圾,需要注意一下。
-- 用来临时存储从起点开始, 牵扯出来的每一层级的关系
create temp table if not exists tmp1( level int, c1 int primary key) ON COMMIT delete rows;
create index if not exists idx_tmp1_1 on tmp1(level, c1);
-- 存储初始层级, 即起点的数据
res := ref[i];
open res for insert into tmp1 select i, c1 from a where c1=v_c1 union select i, unnest(c2) from a
where c1=v_c1 returning *;
return next res;
loop
i := i+1;
-- 已找到所有层级的数据
if i > v_level then
return;
end if;
-- 通过与level=i-1的JOIN推导下一级关系(group by排除重复node(比如1-2-3-4, 1-5-3-4,这里的3会被排除掉)),
-- 通过not exists排除打环的点
res := ref[i];
open res for
insert into tmp1
select t.i, t.c2 from
( select i, unnest(c2) c2 from a join tmp1 tmp on ( a.c1=tmp.c1 and tmp.level=i-1 and a.c1<>v_c1 )
) t
left join tmp1 on (t.c2=tmp1.c1)
where tmp1.* is null group by 1,2
on conflict do nothing
returning *;
return next res;
end loop;
end;
$$ language plpgsql strict;
postgres=# select * from find_rel_cur(1,10);
NOTICE: relation "tmp1" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp1_1" already exists, skipping
find_rel_cur
--------------
a1
a2
a3
a4
a5
a6
a7
a8
a9
a10
(10 rows)
Time: 2.098 ms
postgres=# fetch 1 in a1;
level | c1
-------+-------
1 | 37394
(1 row)
Time: 3.138 ms
postgres=# fetch 1 in a2;
level | c1
-------+----
2 | 0
(1 row)
Time: 1345.473 ms
由于测试模型的问题,第三级搜索了5000万记录, 正常的业务模型不会如此,不必担心
postgres=# fetch 1 in a3; level | c1 -------+---- (0 rows) Time: 15587.686 ms postgres=# fetch 1 in a4; level | c1 -------+---- (0 rows) Time: 0.143 ms postgres=#
UDF优化思路3,异步消息
使用异步消息也可以达到同样的效果。
PostgreSQL是不是很好用呢,异步消息都有啦。
例子
create extension dblink;
CREATE FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER postgresql VALIDATOR postgresql_fdw_validator;
CREATE SERVER dst FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER postgresql OPTIONS (hostaddr '127.0.0.1', port '1921', dbname 'postgres');
CREATE USER MAPPING FOR postgres SERVER dst OPTIONS (user 'postgres', password 'postgres');
create or replace function find_rel_withpath_notify(v_c1 int, v_level int, v_notify_channel text)
returns void as $$
declare
i int := 1;
query text;
ref1 cursor(var1 int, var2 int) for select var1 as level, array[]::int[] || c1 || c2 as path , c1, c2
from (select c1,unnest(c2) as c2 from a where c1=var2) a ;
ref2 cursor(var1 int) for select var1 as level, a.path||a.c2 as path, a.c1, a.c2 from
(select tmp2.path, a.c1, unnest(a.c2) c2 from a join tmp2 on
(a.c1=tmp2.c2 and tmp2.level=i-1 and tmp2.c1<>a.c1)) a;
begin
if v_level <=0 then
raise notice 'level must >=1';
return;
end if;
-- 判断连接是否存在, 不存在则创建.
if array_position(dblink_get_connections(), v_notify_channel) is not null then
else
perform dblink_connect(v_notify_channel, 'dst');
end if;
-- 9.6还是inner temp table,频繁创建和删除,可能导致catalog产生垃圾,需要注意一下。
-- 用来临时存储从起点开始, 牵扯出来的每一层级的关系
-- 目前plpgsql不支持流式返回, 即使使用return next , return query
-- https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.6/static/plpgsql-control-structures.html
create temp table if not exists tmp2(level int, path int[] unique, c1 int, c2 int) ON COMMIT delete rows;
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_1 on tmp2(level, c2);
-- 存储初始层级, 即起点的数据
for rec in ref1(i, v_c1) loop
insert into tmp2 values (rec.level, rec.path, rec.c1, rec.c2) on conflict do nothing;
if found then
query := format($_$select 1 from pg_notify( %L , 'level: %s, path: %s, c1: %s, c2: %s')$_$,
v_notify_channel, rec.level, rec.path, rec.c1, rec.c2);
-- 发送异步消息
perform * from dblink(v_notify_channel, query, true) as t(id int);
end if;
end loop;
loop
i := i+1;
-- 已找到所有层级的数据
if i > v_level then
return;
end if;
-- 通过与level=i-1的JOIN推导下一级关系(group by排除重复node(比如1-2-3-4, 1-2-3-4,完全重复的路径,排除掉。
-- 实际中加了c1,c2唯一约束后不可能存在)),通过not exists排除打环的点
-- path用来表示当前路径,是不是很爽
-- 如果有c1,c2的PK约束,可以不使用group by,直接与tmp2关联
for rec in ref2(i) loop
insert into tmp2 values(rec.level, rec.path, rec.c1, rec.c2) on conflict do nothing;
if found then
query := format($_$select 1 from pg_notify( %L , 'level: %s, path: %s, c1: %s, c2: %s')$_$,
v_notify_channel, rec.level, rec.path, rec.c1, rec.c2);
-- 发送异步消息
perform * from dblink(v_notify_channel, query, true) as t(id int);
end if;
end loop;
end loop;
return;
end;
$$ language plpgsql strict;
在会话a开启一个监听
postgres=# listen hello;
在会话B启动查询
postgres=# select find_rel_withpath_notify(1,5,'hello');
会话A可以读取异步消息
。。。。。。
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,15869}, c1: 32847, c2: 15869" received
from server process with PID 33062.
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,21312}, c1: 32847, c2: 21312" received
from server process with PID 33062.
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,22852}, c1: 32847, c2: 22852" received
from server process with PID 33062.
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,8031}, c1: 32847, c2: 8031" received
from server process with PID 33062.
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,45248}, c1: 32847, c2: 45248" received
from server process with PID 33062.
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,7139}, c1: 32847, c2: 7139" received
from server process with PID 33062.
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,28589}, c1: 32847, c2: 28589" received
from server process with PID 33062.
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,8615}, c1: 32847, c2: 8615" received
from server process with PID 33062.
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,49518}, c1: 32847, c2: 49518" received
from server process with PID 33062.
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,35727}, c1: 32847, c2: 35727" received
from server process with PID 33062.
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,2679}, c1: 32847, c2: 2679" received
from server process with PID 33062.
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,34267}, c1: 32847, c2: 34267" received
from server process with PID 33062.
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,13890}, c1: 32847, c2: 13890" received
from server process with PID 33062.
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,20092}, c1: 32847, c2: 20092" received
from server process with PID 33062.
Asynchronous notification "hello" with payload "level: 2, path: {1,32847,11795}, c1: 32847, c2: 11795" received
from server process with PID 33062.
。。。。。。
设计优化1 - 数组现身
我们在存储关系时,使用的是一对一的存储,这样存储非常简洁,但是也有一定的缺陷,比如要搜索一个用户的直接关系网,就需要搜索N条记录,搜索的层级越多,记录数会成倍增加。
假设平均每个用户有100个直接的关系,那么搜索5级,就得搜索和输出100^1+100^2+100^3+...100^5条记录。
而如果使用数组存储的话,可以将扫描的记录数降低到100^0+100^1+100^2+...100^4条记录,每个层级的开销都差100倍。
用法也很简单,本文就不展示了,数组支持= any(array)的查询,在FUNCTION中支持foreach的循环等。
设计优化2 - 柳暗花明又一春, pgrouting
我们知道关系也有亲密度,事件的关联关系也有相关度的,所以简单的使用有关系和没关系来表示,在现实生活中是远远不够的。
比如,我和小明是好朋友,和少聪是好基友,和PostgreSQL是好基友,这些亲密关系也是完全不同的,在展示的时候,或者在分析人物关系的时候,就体现出来了。
那么怎么表示呢,再加一个字段,表示权重即可。
a(c1, int, c2 int, weight numeric).
在计算路径时,就不是先到先得这么简单了,得计算到每条路径的weight都大于已有的路径才算结束。
例如从A到B,有很多路径,但是第一条路径先到达,不过我们不能就此结束运算,因为还有可能有path总weight更小的,所以需要继续计算,只有当目前每条路径的weight(包括没有达到B的)都超出已计算出来的最短路径时,才结束运算。
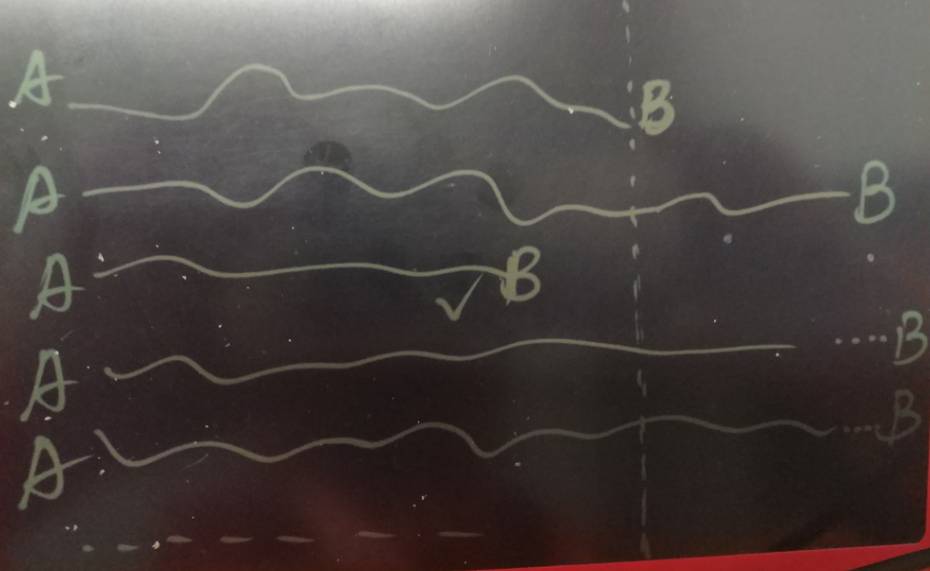
这是pgrouting擅长的,pgrouting完全可以用在图数据库领域。
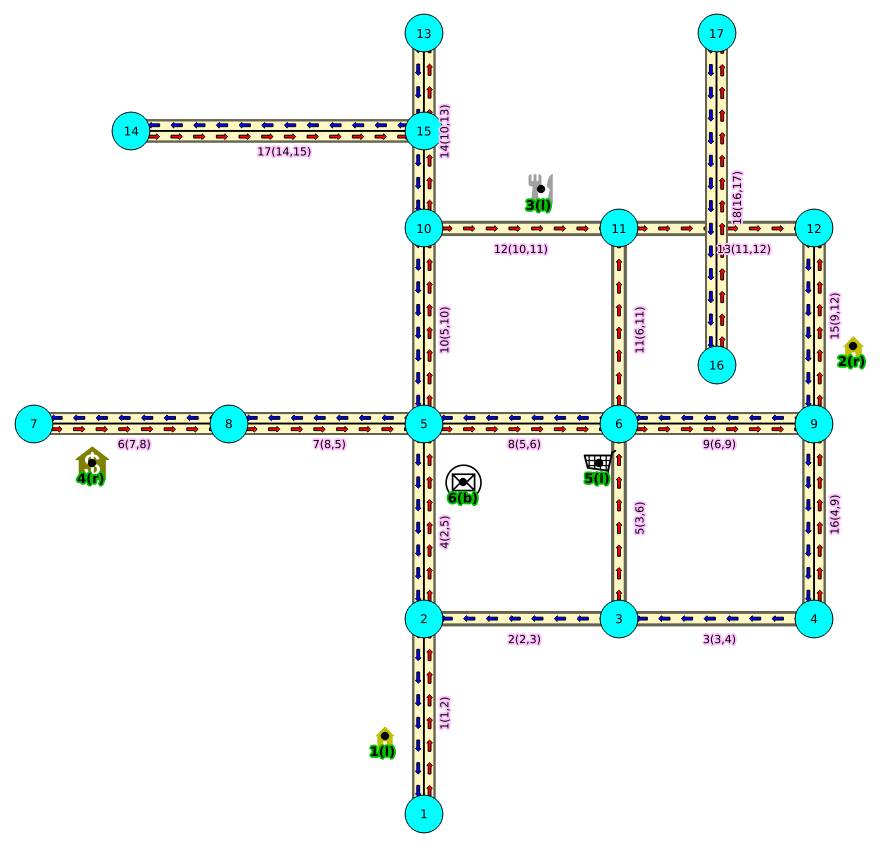
pgrouting天然支持路径的weight(比如路段限速、上坡下坡、道路弯道多少、道路的车道数、道路的拥堵程度,都可以作为动态的weight值),支持多个路径规划算法,支持自定义规划算法。

其他图数据库
neo4j也是非常不错的图数据库,有很多小伙伴在使用。
但是从一些研究论文和PG的对比,可以看出Neo4j也存在一定的问题,比如内存不能装下所有数据时,访问速度不稳定。
Neo4j只能按Label为分组建立索引,进行搜索。(类似分区索引,非全局索引)如果要全局搜索,每个用户必须包含同一个标签。
论文参考:
https://bib.irb.hr/datoteka/690975.1268-4089-1-PB.pdf
https://numergent.com/2015-05/Tropology-performance-PostgreSQL-vs-Neo4j.html
小结
随着人类交流方式、成本越来越低,人与人,人与物,人与事件的交集越来越多,社会关系越来越复杂。
在关系系统中,拥NODE表示点(人,事件,物,加上特定的时间空间属性),NODE与NODE之间有关系的话就将两者关联起来。
关系的数据会继续爆炸性的增长,NODE可能达到万亿级别,每个NODE可能与成千上万的其他NODE发生关系,产生万万亿的关系网。
当然,特定的系统不会有这么庞大的数据,在同一时间点,有万亿级别的关系网已经是非常大的公司才能达到的量级。
PostgreSQL是比较全面的数据库,几乎可以用在任意场景,本文就关系网作为应用场景,使用PostgreSQL的一些特性,设计了一个DEMO,包括关系推导,NODE与NODE的路径搜索等常见需求。
用到的特性举例
1. 数组,用于存储正向关系
2. plpgsql,用于编写推导逻辑,路径搜索逻辑等
3. 游标,用于流式返回
4. 异步消息,用于流式数据返回
4. 聚合查询
5. pgrouting,用于最短路径搜索
6. 递归查询
7. 关于亲密度分析,可以使用类似PostgreSQL rum的插件计算方法,比如计算共同的事件重叠度打分(目前RUM已支持tsvector的近似度值输出和排序,可以用于亲密度计算).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PageRank
rum参考: 《PostgreSQL 全文检索加速 快到没有朋友 - RUM索引接口(潘多拉魔盒)》
亲密度关系层级推导例子
依旧创建1亿用户,每5万作为一个有牵连的群体,每个用户牵连100个亲密用户,形成100亿的关系网。
CREATE EXTENSION rum; create table rum1(c1 int, c2 tsvector, primary key (c1)); create index idx_rum1_1 on rum1 using rum(c2 rum_tsvector_ops); vi test.sql \set id random(1,100000000) insert into rum1 select :id, (select to_tsvector(string_agg(((width_bucket(:id,1,100000000,2000)-1)*50000 + (random()*50000)::int)::text, ' ')) from generate_series(1,100)) on conflict do nothing; pgbench -M prepared -n -r -P 5 -f ./test.sql -c 64 -j 64 -T 100000
通过RUM的rum_tsvector_ops可以按亲近排序,得到同时亲近值。
postgres=# select c1, c2 <=> tsq as dis
from
rum1,
(select to_tsquery(replace(rtrim(ltrim(array_to_tsvector(tsvector_to_array(c2))::text, ''''), ''''),
$$' '$$, ' | ')) tsq from rum1 where c1=1) as tmp
where
c2 @@ tsq
and
c1<>33233490
order by c2 <=> tsq
limit 10;
值越小,关系越亲密
c1 | dis
-------+----------
1 | 0.164493
42469 | 4.11234
28939 | 5.48311
45740 | 5.48311
15508 | 5.48311
11589 | 5.48311
12377 | 5.48311
34282 | 5.48311
16731 | 5.48311
6474 | 5.48311
(10 rows)
Time: 259.834 ms
迭代计算
逐级推导,当然你也可以加个字段实时亲密度,那么就不需要每次都通过rum索引查询了。
create or replace function find_rel_pagerank_cur(
v_c1 int, -- 需要推导的ID
v_level int, -- 推导几级关系
v_rank numeric, -- 亲密度阈值,大于该值的不输出(越大距离越远, 越不亲密)
v_limit_perlevel int -- 每一级输出的最大记录数(如人数)
)
returns setof record as $$
declare
i int := 1;
i_c1 int;
ref cursor(
var_level int,
var_c1 int
) for
select level,c1,c2,pagerank::numeric from
(select var_level as level, var_c1 as c1, c1 as c2, c2 <=> tsq as pagerank from
rum1,
(select to_tsquery(replace(rtrim(ltrim(array_to_tsvector(tsvector_to_array(c2))::text, ''''), ''''),
$_$' '$_$, ' | ')) tsq from rum1 where c1=var_c1) as tmp
where
c2 @@ tsq
and
c1<>var_c1
order by c2 <=> tsq
limit v_limit_perlevel
) t where t.pagerank < v_rank ;
begin
if v_level <=0 then
raise notice 'level must >=1';
return;
end if;
-- 9.6还是inner temp table,频繁创建和删除,可能导致catalog产生垃圾,需要注意一下。
-- 用来临时存储从起点开始, 牵扯出来的每一层级的关系
-- 目前plpgsql不支持流式返回, 即使使用return next , return query
-- https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.6/static/plpgsql-control-structures.html
create temp table if not exists tmp2(level int, c1 int, c2 int, pagerank numeric, primary key(c1,c2))
ON COMMIT delete rows;
create index if not exists idx_tmp2_1 on tmp2(level, c2);
-- 存储初始层级, 即起点的数据
for rec in ref(i,v_c1) loop
insert into tmp2 values (rec.level, rec.c1, rec.c2, rec.pagerank) on conflict do nothing;
if found then
raise notice 'level: %, c1: %, c2:% ,pagerank: %', rec.level, rec.c1, rec.c2, rec.pagerank;
return next rec;
end if;
end loop;
loop
i := i+1;
-- 已找到所有层级的数据
if i > v_level then
return;
end if;
for i_c1 in select t2.c1 from rum1 t2 JOIN tmp2 t1 on (t1.c2=t2.c1 and t1.level=i-1 and t2.c1<>v_c1)
where not exists (select 1 from tmp2 where tmp2.c1=t2.c1) group by 1
loop
for rec in ref(i,i_c1) loop
insert into tmp2 values (rec.level, rec.c1, rec.c2, rec.pagerank) on conflict do nothing;
if found then
raise notice 'level: %, c1: %, c2:% ,pagerank: %', rec.level, rec.c1, rec.c2, rec.pagerank;
return next rec;
end if;
end loop;
end loop;
end loop;
return;
end;
$$ language plpgsql strict;
postgres=# select * from find_rel_pagerank_cur(96807211,2,10000,10) as t(level int, c1 int, c2 int, pagerank numeric);
NOTICE: relation "tmp2" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: relation "idx_tmp2_1" already exists, skipping
NOTICE: level: 1, c1: 96807211, c2:96810420 ,pagerank: 5.48311
NOTICE: level: 1, c1: 96807211, c2:96849305 ,pagerank: 5.48311
NOTICE: level: 1, c1: 96807211, c2:96810740 ,pagerank: 5.48311
NOTICE: level: 1, c1: 96807211, c2:96839717 ,pagerank: 5.48311
NOTICE: level: 1, c1: 96807211, c2:96849378 ,pagerank: 5.48311
NOTICE: level: 1, c1: 96807211, c2:96800097 ,pagerank: 5.48311
NOTICE: level: 1, c1: 96807211, c2:96832351 ,pagerank: 5.48311
NOTICE: level: 1, c1: 96807211, c2:96839438 ,pagerank: 5.48311
NOTICE: level: 1, c1: 96807211, c2:96816466 ,pagerank: 5.48311
NOTICE: level: 1, c1: 96807211, c2:96836416 ,pagerank: 5.48311
NOTICE: level: 2, c1: 96800097, c2:96812430 ,pagerank: 4.11234
NOTICE: level: 2, c1: 96800097, c2:96802051 ,pagerank: 5.48311
NOTICE: level: 2, c1: 96800097, c2:96824209 ,pagerank: 5.48311
......
PostgreSQL值得改进的点
1. insert into .. returning .. 游标支持流式返回, 目前需要等insert结束才返回returning的结果, 无法同时插入同时return
2. with recursive 递归查询目前仅支持支持work table中间状态的查询,建议支持全量work table查询。
3. with recursive 递归查询,建议支持LOOPth的变量,知道进入第几个循环了。
4. plpgsql return next, return query支持流式返回。 (目前要在FUNCTION中返回流式数据,还只能写C的接口,手册中有指出,未来可能会对plpgsql添加流式返回的支持)
5. 可以增强的点,PostgreSQL的索引接口是完全开放的,索引存储怎么组织,怎么检索,用户都可以自定义。
针对图类数据应用,还有更多可以发掘的效率提升点,比如目前亲密度的关系是指一度关系的亲密度打分(可以走RUM的相似度排序接口,很快),
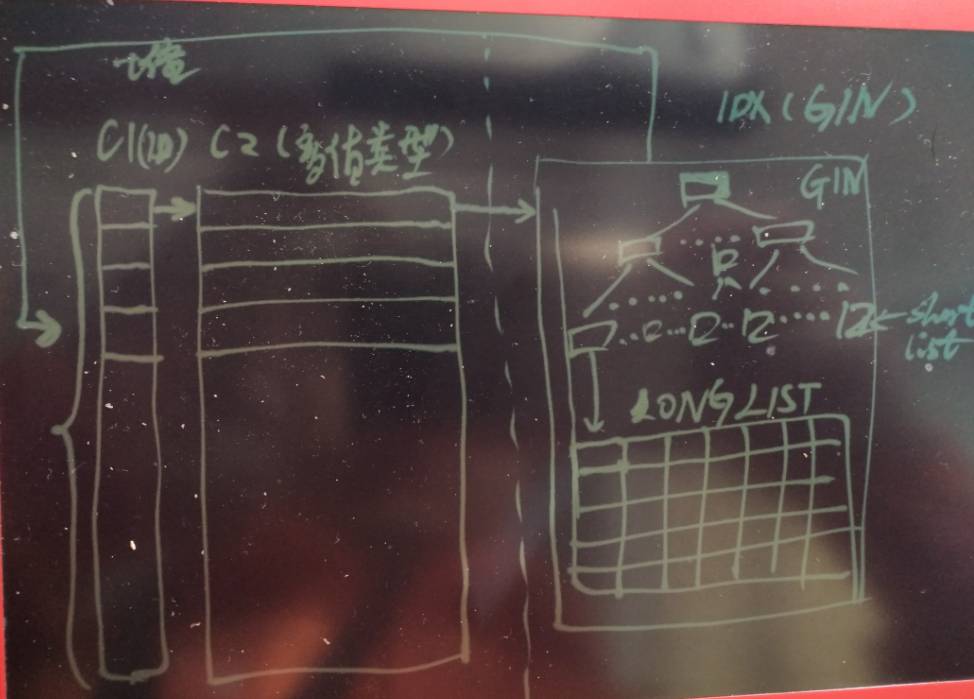
但是怎么针对二度,甚至更广度的打分,还能做到高效呢?
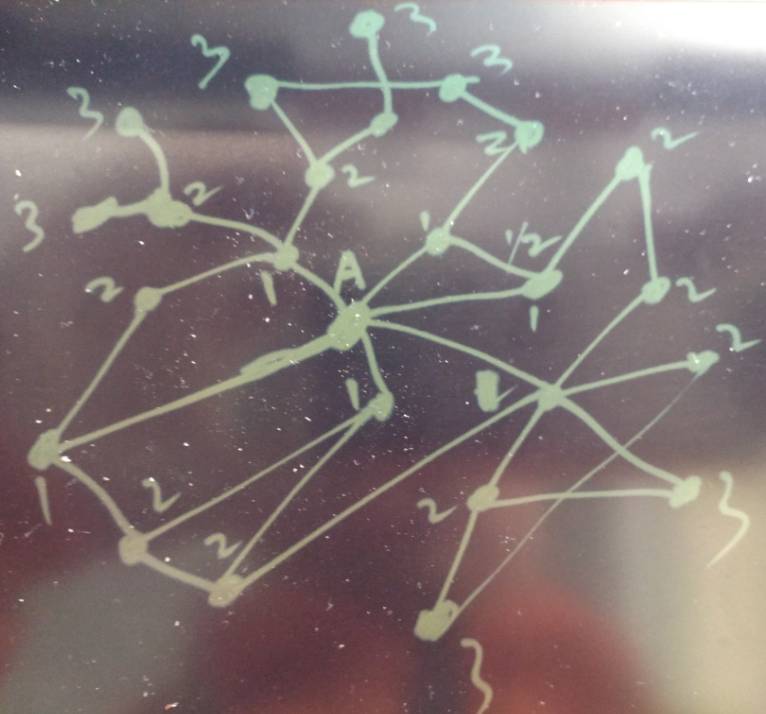
按一度的方法,多轮检索查询效率肯定不高。
这个时候就体现PostgreSQL开放接口的优势了,用户完全可以根据场景,自定义更高效的索引组织,结构。
可以参考rum, bloom index的写法。 https://github.com/postgrespro/rum https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.6/static/xindex.html https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.6/static/bloom.html
参考
1. neo4j
2. 基于PG的graph database
http://blog.163.com/digoal@126/blog/static/16387704020160182738756/
https://github.com/google/cayley
3. pgrouting
http://pgrouting.org/
http://docs.pgrouting.org/2.3/en/doc/index.html
pgrouting 与双十一的物流路径规划
《聊一聊双十一背后的技术 - 物流, 动态路径规划》
4. PostgreSQL facebook linkbench社交关系模型性能测试
https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/60731
5. 递归查询的几个例子
《distinct xx和count(distinct xx)的变态递归优化方法 - 索引收敛(skip scan)扫描》
《用PostgreSQL找回618秒逝去的青春 - 递归收敛优化》

请在登录后发表评论,否则无法保存。
